There are two main types of forex brokers:
1. Dealing Desks (DD)
2. No Dealing Desks (NDD).
Dealing Desk brokers are also called Market Makers.
No Dealing Desks can be further subdivided into:
1. Straight Through Processing (STP) and
2. Electronic Communication Network + Straight Through Processing (ECN+STP).
A dealing desk broker – also known as a ‘market maker’ – will take trades from its clients without necessarily trading in the underlying market itself. They will offer a quote based on the underlying market price, and then sit on the other side of the client’s trade.
When a dealing desk broker accepts a trade, they may or may not trade in the underlying market to cover their exposure. They may also offset this exposure with other clients’ opposing trades that are similarly kept ‘in house’. This practice of keeping trades in house is known as running a ‘B book’, and it enables dealing desk brokers to keep all of the profit on its clients’ losing trades.
Let’s say you place a buy order for EUR/USD for 100,000 units with your Dealing Desk broker.
To fill you, your broker will first try to find a matching sell order from its other clients or pass your trades on to its liquidity provider, i.e. a sizable entity that readily buys or sells a financial asset. By doing this, they minimize risk, as they earn from the spread without taking the opposite side of your trade. However, in the event that there are no matching orders, they will have to take the opposite side of your trade.
When a company says it has a ‘no dealing desk policy’ it means that it provides trading with immediate execution in the underlying market.
This is different from trading through a dealing desk, where the broker is likely to remain on the other side of your trade. With the ‘no dealing desk’ model, the broker offsets its exposure on its clients’ trades by matching each trade in full in the underlying market. When there is no dealing desk, the company might only profit from the dealing spread per trade. They will have no financial interest in whether your trade makes or loses money. You will have access to a high-liquidity pool full of competitive bid and ask prices, and you will know that – whatever position you take – your broker is not taking a position against you.
STP brokers or Straight Through Processing brokers, is the name given to brokers that, when upon receipt of a client order, will pass on the orders directly to their liquidity provider. Liquidity providers can include a Bank, a Hedge Fund, Investment corporations or another broker and as such no intermediary in the order will be involved – in other words the STP broker will not be filtering the orders through a Dealing Desk. The absence of a Dealing Desk intervention is what makes the broker’s electronic trading platform STP.
With the absence of such an intermediary process (dealing desk) the STP broker will be able to process its client’s orders without any delay and in addition the STP broker will not send re-quotes to its clients something that most investors will regard as a huge advantage, as the STP broker in effect will allow its clients to trade during the release times of financial news without any restrictions.
STP brokers benefit from having several liquidity providers as an increase in the number of providers in the system means the better the fills for the client. A large number of STP brokers will use banks, which trade on the Interbank market (the top-level foreign exchange market where banks exchange different currencies) as their liquidity providers. Let’s say your NDD STP broker has four different liquidity providers. In their system, they will see four different pairs of bid and ask quotes.
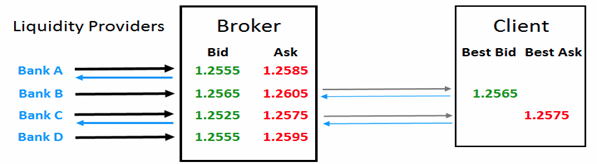
Their system then sorts these bid and ask quotes from best to worst. In this case, the best price in the bid side is 1.2565 (you want to sell high) and the best price on the ask side is 1.2575 (you want to buy low). Your broker will add a small, usually fixed, markup, if their policy is to add a 1-pip markup.
So when you decide to buy 100,000 units of EUR/USD at 1.2575, your order is sent through your broker and then routed to either Bank C or A. This changing bid/ask quote is also the reason why most STP type brokers have variable spreads. If the spreads of their liquidity providers widen, they have no choice but to widen their spreads too.
An ECN broker is a forex financial expert that uses electronic communications networks (ECNs) to give clients direct access to other participants in currency markets. Because an ECN broker consolidates price quotations from several market participants, it can generally offer its clients tighter bid/ask spreads than would be otherwise available to them.
ECN brokers are non-dealing desk brokers, meaning that they do not pass on order flow to market makers. Instead, they match participants in a trade electronically and pass the orders to liquidity providers. Since an ECN broker only matches trades between market participants, it cannot trade against the client, an allegation often directed against some unscrupulous retail forex brokers. Because ECN spreads are much narrower than those used by everyday brokers, ECN brokers charge clients a fixed commission per transaction.
An ECN broker facilitates trades for interested investors across the ECN. Working with brokers of this nature often results in lower fees as well as additional trading time availability because of how the ECN functions.
Usually, day traders and scalpers prefer the tighter spreads because it is easier to take small profits as the market needs less ground to cover to get over transaction costs.
Meanwhile, wider spreads tend to be insignificant to longer term swing or position traders.
Below we have added a summary of the major differences between Market Makers, STP brokers, and STP+ECN brokers:
|
COMPARISON |
DEALING DESK (MARKET MAKER) |
NO DEALING DESK (STP) |
NO DEALING DESK (ECN+STP) |
|
Spread |
Fixed Spreads |
Variable spreads |
Variable spreads and/or commission fees |
|
Order Execution |
Take the opposite side of your trade |
Simply a bridge between client and liquidity provider |
A bridge between client and liquidity provider and other ECN participants |
|
Quote Prices |
Artificial quotes |
Prices come from liquidity providers |
Prices come from liquidity providers and other ECN participants |
|
Order Filling |
Orders are filled by broker on a discretionary basis |
Automatic execution, no re-quotes |
Automatic execution, no re-quotes |
|
Real Market Info |
NA |
NA |
Displays the Depth of Market (DOM) or liquidity information |
*The information presented above is intended for informative and educational purposes, should not be considered as investment advice, or an offer or solicitation for a transaction in any financial instrument and thus should not be treated as such. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.

2021開羅投資博覽會
2022年終極金融科技獎
2022歐洲金融科技
2023全球外匯獎
版權所有 © 2024
Soho Markets LLC在聖文森特和格林納丁斯註冊為國際商業公司( International Business Company ),註冊號為1310 LLC 2021 。
風險提示:差價合約( CFDs )是複雜的工具,由於槓桿加持,會給您帶來較高的迅速虧損風險。請您考慮是否了解差價合約( CFDs )的原理,以及是否能夠承擔較高的虧損風險。請閱讀完整的風險披露
區域限制: SOHO MARKETS GLOBAL LIMITED不為美國、加拿大、以色列、日本、朝鮮、比利時和聯合國/歐盟制裁國家提供服務
CLIENT AGREEMENT (TERMS AND CONDITIONS) Privacy Policy Risk Disclosure